Choosing between cloud and on-premise solutions is critical for financial institutions aiming to meet the EU Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) requirements. Here's what you need to know:
- Cloud Solutions: Offer flexibility, scalability, and built-in tools for compliance and disaster recovery. However, they depend on vendor reliability and require careful management of data residency and third-party risks.
- On-Premise Solutions: Provide full control over data and infrastructure, making them ideal for strict regulatory environments. They come with higher upfront costs, limited scalability, and greater maintenance demands.
- Hybrid Models: Combine the best of both, allowing sensitive data to remain on-premise while leveraging cloud services for scalability and reporting.
Quick Comparison
| Factor | Cloud Solutions | On-Premise Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Costs | Lower (subscription-based) | Higher (infrastructure setup) |
| Scalability | Easy and fast | Limited by hardware |
| Data Control | Shared responsibility with vendors | Full control |
| Maintenance | Managed by vendors | Requires in-house IT teams |
| Disaster Recovery | Built-in redundancy | Needs separate infrastructure |
| Customization | Limited by vendor capabilities | Highly customizable |
Key Takeaway: Small institutions often benefit from cloud setups, large enterprises lean toward on-premise or hybrid models, and medium-sized entities find hybrid solutions most practical. The right choice depends on your institution's size, budget, and compliance priorities.
DORA in Atlassian Cloud: An Expert Approach to Compliance
Factors for DORA Compliance
Financial institutions need to consider several key aspects when choosing solutions to meet DORA compliance requirements. These choices directly affect their ability to adhere to regulations while keeping operations efficient.
Data Security and Privacy
Meeting DORA and GDPR standards means implementing strong security measures. Some of the essentials include:
- End-to-end encryption for data both in transit and at rest
- Multi-factor authentication to ensure secure access
- Regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities
The decision between cloud-based or on-premise solutions plays a big role in how these security measures are applied.
Disaster Recovery and Incident Response
The recovery and response capabilities of cloud and on-premise solutions vary significantly. Here's a quick comparison:
| Requirement | Cloud Solution | On-Premise Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Recovery Time | Automated, often quicker | Relies on internal resources |
| System Resilience | Built-in redundancy, AI-driven tools | Requires separate infrastructure |
| Cost Structure | Subscription-based | Higher upfront costs |
Managing Third-Party Risks
Third-party risks require close attention through vendor evaluations, clear agreements, and regular checks. Key steps include:
- Conducting detailed risk assessments for vendors
- Drafting clear contracts that outline responsibilities
- Regularly monitoring and auditing third-party services
- Keeping thorough records of vendor compliance with DORA standards
You can read more about managing Third-Party risks in our article titled Top 5 ICT Third-Party Risk Management Best Practices.
Reporting and Audit Needs
The effectiveness of reporting depends heavily on the solution's design. Financial institutions need to track and document:
- System access and changes made
- Security incidents and how they were handled
- Interactions with third-party vendors
- Compliance verification activities
Cloud solutions often come with built-in reporting tools, making them easier to use. On-premise systems might need extra setup but allow for more customization.
These factors highlight the importance of carefully weighing the pros and cons of cloud versus on-premise solutions. Each option offers distinct advantages depending on an institution's specific needs.
Cloud Solutions for DORA Compliance
Cloud-based platforms have become essential for financial institutions aiming to meet DORA requirements. These solutions are designed to handle the intricate demands of digital operational resilience, offering tools that simplify compliance management.
Benefits and Challenges of Cloud Solutions
| Aspect | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Flexible scaling | Relies on stable internet connectivity |
| Security | Built-in protection features | Ensuring data residency compliance in the EU |
| Cost | Lower upfront and ongoing costs | Potential for vendor lock-in |
| Maintenance | Automatic updates for compliance | Requires vendor-neutral strategies |
According to IDC:
65% of major enterprises will mandate data sovereignty controls from their cloud service providers to adhere to data protection and privacy regulatory requirements [3]
Example: DORApp
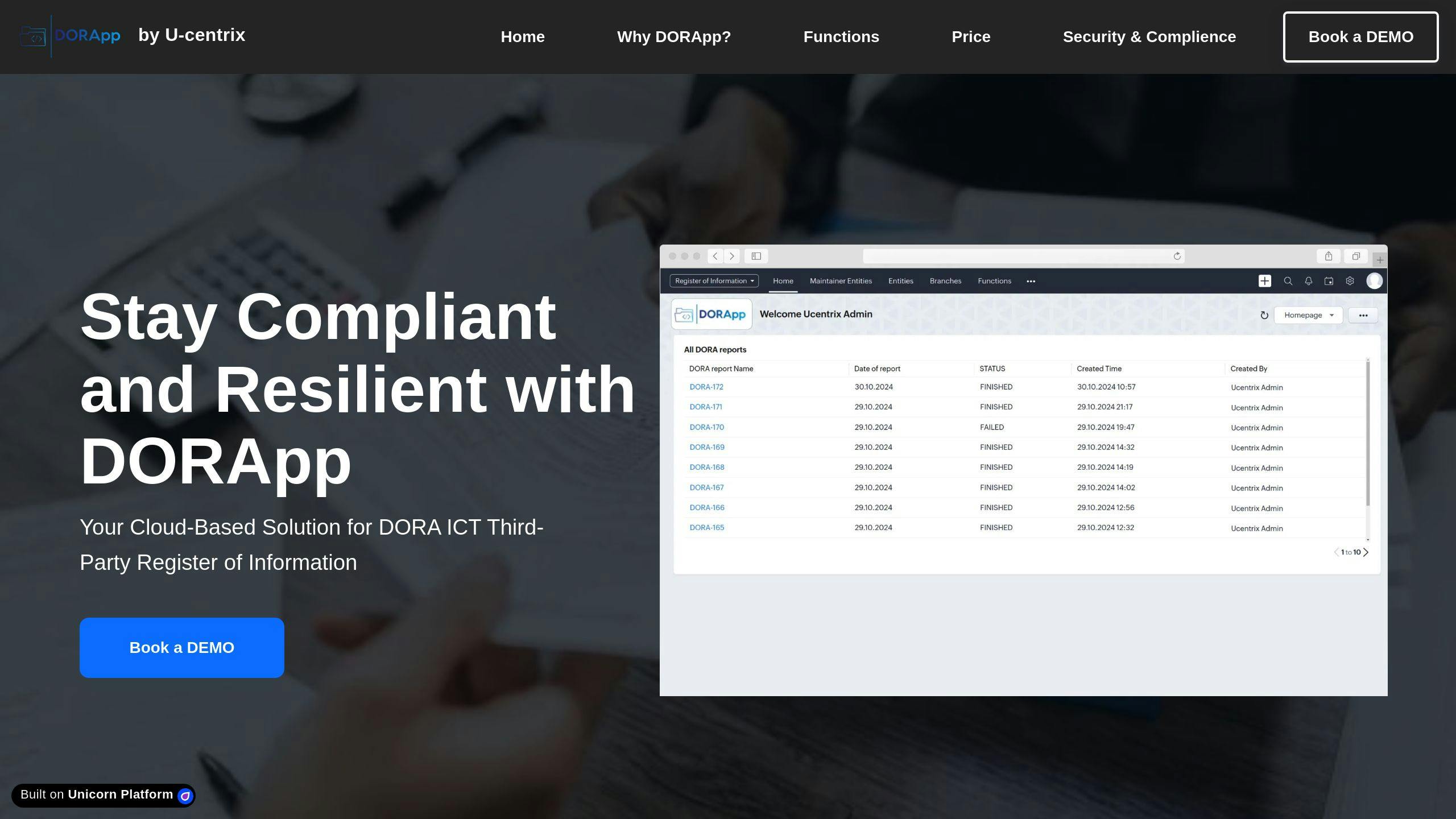
DORApp is a great example of how a cloud solution can address DORA requirements effectively. It offers features like:
- Audit logging to track data changes
- Storage of data in EU data center’s
- Multi-factor authentication
- Scalability and availability guarantee
- Enterprise level customer support
- Data export of all financial institution’s data to relieve the Vendor Lock in effect
- Integration with on-prem systems
Matt Adams, Enterprise Security Architect at Santander, explains:
Scalability and monitoring are at an arm's length - now I can just go to an API, take the data I need, and slice and dice it in any way [2]
While cloud platforms bring automation and flexibility, on-premise systems remain a traditional choice for institutions that prioritize control and customization.
On-Premise Solutions for DORA Compliance
On-premise solutions give financial institutions full control over their infrastructure and data, making them a strong option for meeting DORA compliance requirements. Weighing their advantages and challenges is key when comparing them to cloud or hybrid setups.
Benefits of On-Premise Solutions
On-premise setups provide several clear advantages, particularly when it comes to data control and meeting regulatory demands.
| Benefit Category | Impact on DORA Compliance |
|---|---|
| Data Control | Full ownership of infrastructure strengthens security and privacy compliance |
| Customization | Solutions can be tailored to meet specific regulatory requirements |
| Third-Party Risk | Minimizes reliance on external providers, simplifying risk management |
| Security | Direct oversight of data protection measures |
Institutions using on-premise systems can implement custom security practices that ensure alignment with both DORA and GDPR. For instance, the 21 Travel Rule allows Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs) to keep sensitive customer data stored internally, enhancing data sovereignty [4].
Challenges of On-Premise Solutions
While on-premise solutions offer control and customization, they also come with notable challenges:
- High initial costs for infrastructure setup and ongoing maintenance
- Resource demands, requiring dedicated IT teams for upkeep
- Limited scalability compared to the flexibility of cloud solutions
Disaster recovery is another area where on-premise systems can fall short. Unlike cloud-based redundancy, these systems need dedicated infrastructure for backup and recovery, which can be both expensive and time-consuming. Institutions must also ensure that their disaster recovery plans meet DORA's strict requirements, such as the 24-hour incident notification rule [4].
Integration with existing ICT systems can be more complex than with cloud solutions. However, this complexity can be mitigated by the ability to design highly specific implementations. Despite these hurdles, on-premise solutions remain a strong option for organizations that prioritize control and customization, especially when combined with hybrid models.
sbb-itb-107f699
Comparison: Cloud vs. On-Premise Solutions
When deciding on solutions for DORA compliance, financial institutions need to carefully consider the differences between cloud and on-premise setups. According to Gartner, cloud services can lower initial costs by up to 50%, but operational expenses, such as subscription fees and scaling, may increase by 20-30% over five years [1].
| Factor | Cloud Solutions | On-Premise Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Lower upfront costs with a pay-as-you-go model | Higher upfront costs for infrastructure |
| Long-term Costs | Operational costs can add up over time | More cost-efficient after the initial investment |
| Scalability | Quick and easy resource scaling | Limited by physical hardware |
| Security Control | Shared responsibility with the vendor | Full control over security |
| Maintenance | Managed by the vendor | Requires in-house IT resources |
| Customization | Restricted to vendor capabilities | Highly customizable |
| Disaster Recovery | Built-in redundancy and failover options | Needs separate infrastructure |
| Third-Party Risk | Higher due to reliance on vendors | Minimal external dependencies |
Security, Compliance, and Integration
On-premise solutions offer full control, making them a strong choice for meeting DORA's strict data handling requirements. On the other hand, cloud providers like AWS and Azure simplify integration with automated tools, though institutions must weigh the risks of vendor dependency against operational flexibility [1].
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Cloud solutions shine with their low upfront costs, but long-term subscription expenses can add up. On-premise systems, while requiring significant initial investment, may prove more economical in the long run. The trade-offs detailed in the table illustrate the critical need to align technology choices with long-term business objectives.
Cloud systems also stand out in disaster recovery, offering built-in redundancy, while on-premise setups demand dedicated infrastructure. For added flexibility, many enterprises are using multiple cloud providers to meet DORA requirements.
To balance the advantages of both models, many organizations are turning to hybrid solutions, which combine flexibility with greater control.
Hybrid Solutions and Recommendations
What Are Hybrid Solutions?
Hybrid solutions for DORA compliance offer a mix of on-premise control for sensitive data and the scalability of cloud services. These setups let organizations keep critical data and core banking operations on-premise while leveraging the cloud for tasks that require flexibility and scale. This approach supports DORA's focus on operational resilience by combining strict data control with scalable reporting capabilities.
Choosing the Right Solution
When deciding between cloud, on-premise, or hybrid setups, financial institutions need to assess their operational needs carefully. A hybrid approach often requires striking the right balance to meet compliance goals effectively.
| Factor | Small Institutions | Medium-Sized Entities | Large Organizations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Budget Considerations | Cloud-first approach for lower upfront costs | Hybrid model with selective cloud use | Comprehensive hybrid infrastructure |
| Data Control Needs | Basic on-premise storage for critical data | Mixed storage strategy | Advanced data sovereignty controls |
| Compliance Requirements | Standard cloud compliance features | Custom hybrid compliance framework | Complex multi-jurisdiction compliance |
| Resource Availability | Limited IT staff favors cloud solutions | Balanced IT team for hybrid management | Dedicated teams for each environment |
The following example highlights how a hybrid strategy can address both compliance and operational demands.
Case Study: Hybrid Implementation
In 2024, a mid-sized European bank successfully adopted a hybrid model, showcasing the advantages of combining on-premise and cloud systems. The bank kept its core banking systems and customer data on-premise while using cloud services for customer-facing applications and reporting tools. Key outcomes included:
- A 30% drop in operational costs
- Improved disaster recovery and compliance reporting with 99.99% uptime
- Enhanced security through integrated control measures
This strategy enabled the bank to fully meet DORA's rigorous standards for operational continuity and data protection.
"For most modern enterprises, the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of cloud-based solutions make them the preferred choice", say experts at Aavenir CLM. "However, the key to successful DORA compliance lies in finding the right balance between cloud scalability and on-premise control."
With a hybrid setup, financial institutions can maintain strict oversight of sensitive operations while tapping into cloud-based advancements. For instance, platforms like DORApp can support DORA-compliant reporting, while critical financial data remains securely stored on-premise.
Key Implementation Considerations:
- Seamless integration between cloud and on-premise systems
- Strong security measures across all environments
- Clear and enforceable data storage policies
- Regular audits and robust disaster recovery plans
Conclusion
As financial institutions prepare for DORA compliance in 2025, deciding between cloud and on-premise solutions hinges on factors like organization size, operational demands, and regulatory priorities. Cloud platforms excel in flexibility and cost management, while on-premise systems offer unparalleled control. This has made hybrid solutions an appealing middle ground for many.
The best approach depends on each organization's specific needs. Cloud-based platforms, for instance, have shown great flexibility in meeting changing regulatory standards while keeping costs manageable [1]. However, the effectiveness of these platforms often varies based on the size of the institution:
| Organization Size | Recommended Primary Approach |
|---|---|
| Small Institutions | Cloud-Based |
| Medium Organizations | Hybrid |
| Large Enterprises | Custom Hybrid/On-Premise |
On-premise systems remain a strong choice for institutions requiring strict data sovereignty and full control over their infrastructure. This is especially critical for banks and financial firms operating across multiple jurisdictions or handling sensitive data under GDPR and DORA regulations [4].
Hybrid solutions are gaining traction as they address both compliance and operational challenges. For example, RackWare's multi-cloud strategies have proven effective for improving disaster recovery and meeting compliance needs [3].
When choosing a solution, financial institutions should focus on these key areas:
- Operational Resilience: Ensuring services remain available and disaster recovery plans are robust.
- Regulatory Flexibility: Staying compliant with DORA and other evolving regulations.
- Scalable Costs: Aligning technology investments with organizational growth.
- Integrated Security: Applying strong security measures across all platforms.
Ultimately, the ideal approach isn't about picking one solution over another but finding the right mix of technologies that meet regulatory demands, operational goals, and future growth plans. By doing so, financial institutions can remain resilient in the face of changing regulations and operational challenges [4][1].
FAQs
What sets cloud solutions apart from on-premise options for DORA compliance?
DORA outlines specific rules for financial institutions using technology. In cloud setups, EU regulators oversee key ICT providers, such as major cloud platforms. Cloud solutions often come with lower upfront costs and more flexibility, but they require a strong focus on data sovereignty and security. On-premise solutions, on the other hand, give organizations full control over their data and compliance efforts but need a larger initial investment and more resources to manage.
What should organizations keep in mind for hybrid setups?
Hybrid solutions blend cloud convenience with on-premise control, making them an effective option for DORA compliance. For instance, financial institutions might store sensitive customer data on-premise while leveraging cloud tools for analytics or reporting. This approach balances operational efficiency with meeting regulatory demands.
How can third-party risks be managed effectively?
Managing risks tied to third-party providers is crucial, especially when using cloud or hybrid solutions. Organizations should focus on:
- Conducting regular security evaluations of vendors
- Defining clear compliance responsibilities in contracts
- Continuously monitoring service quality
- Keeping detailed records of all risk management efforts
- Ensuring risk controls are integrated across both cloud and on-premise systems
What are the disaster recovery expectations?
DORA emphasizes operational resilience, including strong disaster recovery plans. Key priorities include:
- Complying with the 24-hour incident notification rule
- Setting up automated recovery systems
- Regularly testing recovery procedures
- Documenting all recovery processes clearly
These FAQs highlight essential points, but your institution's specific operational and regulatory needs should guide your approach.


