Banks in the EU must comply with DORA starting January 17, 2025. This regulation enforces stricter operational resilience and cybersecurity standards. To meet these demands, banks need GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) software that automates compliance, manages risks, and tracks vendor relationships.
Key Highlights:
- DORA Compliance Requirements:
- Incident reports: Initial (24 hours), Intermediate (72 hours), Final (1 month).
- Non-compliance fines: Up to 2% of annual turnover.
- GRC Software Must-Haves:
- Automated risk assessments and compliance tracking.
- Third-party vendor oversight tools.
- Real-time monitoring and detailed audit capabilities.
- Top Solution: DORApp
- Automated XBRL reporting.
- EU-hosted secure infrastructure.
- Quick deployment and cost-effective (€200/user/month).
- AI and Live Monitoring Trends:
- AI enhances compliance accuracy and risk detection.
- Real-time monitoring ensures continuous compliance.
Quick Comparison:
| Feature | DORApp Enterprise | Traditional GRC Platforms | Excel-Based Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| DORA Compliance | Automated XBRL reporting | Manual adaptation required | Manual data entry |
| Pricing | €200/user/month | Varies by provider | Low upfront cost |
| Security | EU-based, ISO27001 | Varies by provider | Limited protection |
| Implementation | Quick deployment | 3–6 months | Immediate but manual |
| Automation | High | Medium | Minimal |
Banks should prioritize GRC tools that simplify compliance, reduce manual work, and enhance operational resilience.
Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) Compliance through Vendor and Contract Management
Must-Have GRC Software Features
Modern GRC software for EU banks needs to align with DORA requirements while simplifying risk management processes.
Risk and Compliance Tools
Banks face increasing pressure to handle risk and compliance efficiently to meet regulatory demands. For example, MetricStream's system at Zurich Insurance shows how automated workflows can streamline compliance tasks.
Here’s what’s essential:
Automated Risk Assessment
- Real-time monitoring of risks
- AI-powered updates on regulations
- Tools for control monitoring
- Risk analysis features
Compliance Tracking
- XBRL reporting capabilities
- Policy management systems
- Alerts for regulatory changes
- Tools to identify and address compliance gaps
Banks must also address risks from external vendors as part of their overall risk strategy.
Third-Party Risk Tools
Managing third-party vendors is just as critical as internal risk controls. With 97% of major U.S. banks reporting breaches tied to external vendors last year, vendor oversight is no longer optional.
| Feature | Purpose | DORA Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Vendor Registry | Centralized database of ICT providers | Mandatory documentation |
| Risk Assessment | Evaluates provider reliability | Pre-contract due diligence |
| Performance Monitoring | Tracks vendor compliance | Continuous oversight |
| Contingency Planning | Backup provider arrangements | Operational resilience |
"Compliance with DORA offers significant benefits to those who adhere to its explicit requirements and underlying principles. The economic advantages are substantial, leading to improved decision-making and avoiding the costs associated with neglecting known threats."
– Rois Ni Thuama, head of cyber governance at Red Sift
Data Security and Audit Tools
Effective GRC software also needs to prioritize data security. With the average cost of data breaches hitting $4.5 million in 2024, security and audit tools are non-negotiable.
Security Controls
- Zero-Trust Architecture
- Encryption protocols
- Access management systems
- Real-time attack monitoring
Audit Capabilities
- Comprehensive audit trails
- Tools for evidence collection
- Compliance reporting features
- Incident documentation systems
ServiceNow’s GRC platform highlights these needs, offering no-code playbooks and intelligent chatbots for immediate support. The software must not only stop data breaches but also keep detailed audit trails for reporting. This aligns with DORA’s focus on operational resilience and cybersecurity.
Leading GRC Software for EU Banks
With regulations constantly evolving, EU banks need specialized GRC software to stay compliant. Advanced tools like DORApp simplify compliance and risk management, meeting the demands of modern banking.
DORApp
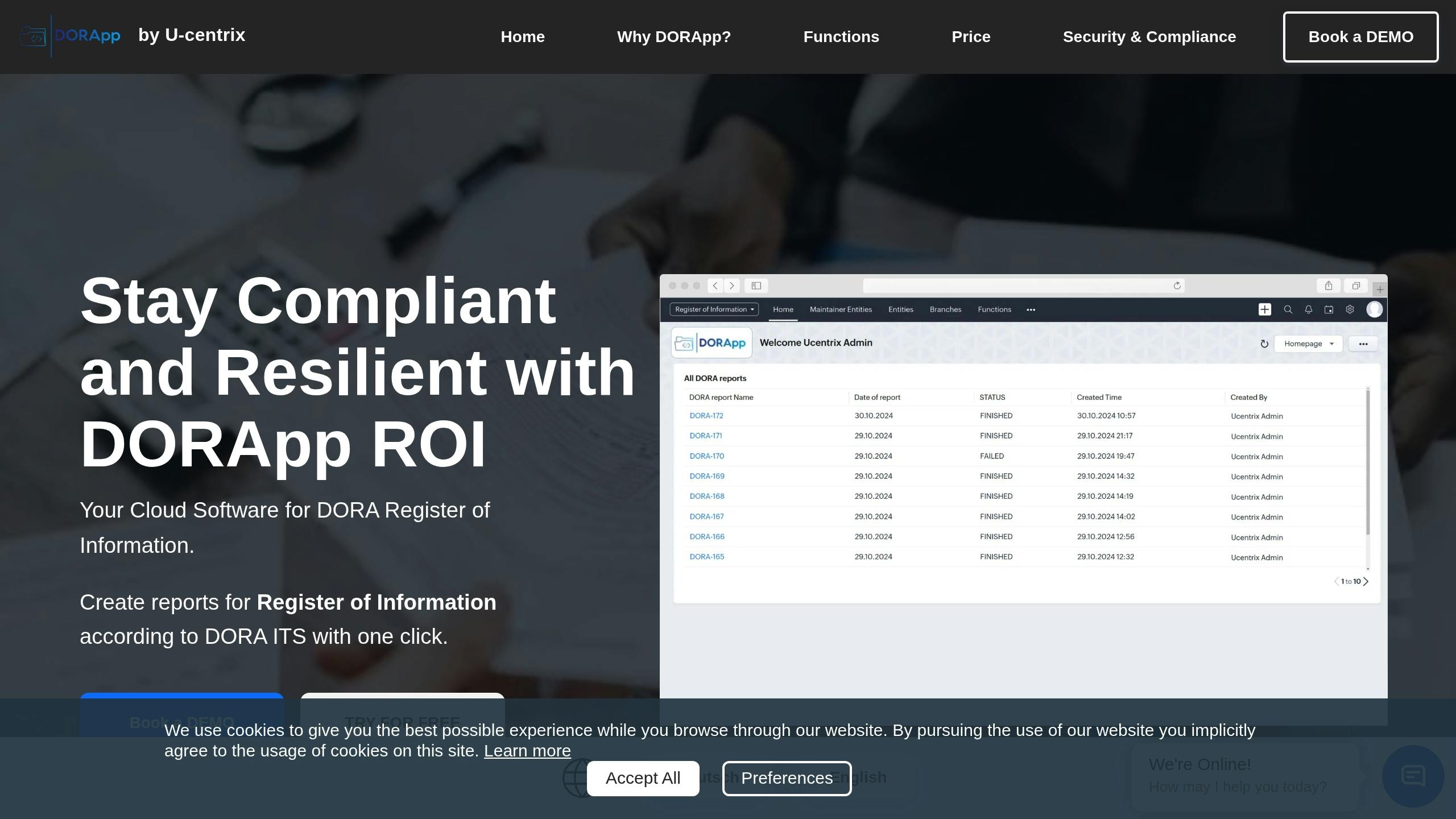
DORApp is a leading SaaS platform designed to meet the stringent requirements of DORA compliance for EU financial institutions. It excels in automating XBRL reporting and managing data efficiently.
Key Features:
- Automated XBRL reporting aligned with DORA standards
- Intelligent data enrichment leveraging the LEI register
- Comprehensive management of ICT third-party providers
- Secure cloud infrastructure hosted in the EU
- Multi-factor authentication and IP filtering
These capabilities directly tackle DORA's regulatory requirements, ensuring compliance is both accurate and efficient.
In 2023, Kieler Rückversicherung successfully adopted DORApp. Martin Steinbach, their Head of IT, shared:
"I was initially doubtful if DORApp could be tailored quickly to our needs. It delivered a polished reporting platform perfectly aligned with our requirements."
DORApp stands out for its automation, security, and quick implementation, making it a preferred choice among EU banks.
GRC Software Comparison
Selecting the right GRC platform requires a close look at the features and benefits of available solutions. Here's a comparison of DORApp with other options:
| Feature Category | DORApp Enterprise | Traditional GRC Platforms | Excel-Based Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| DORA Compliance | Built-in XBRL generation | Requires manual adaptation | Manual data entry |
| Pricing Model | €200/user/month | Variable licensing costs | Low upfront cost |
| Data Security | EU-based, ISO27001 certified | Varies by provider | Limited protection |
| Implementation Time | Quick deployment | 3–6 months on average | Immediate but manual |
| Automation Level | Fully automated | Partially automated | Minimal automation |
DORApp's automation reduces manual work and errors while ensuring data security and compliance with GDPR. Features like automated LEI verification, real-time compliance tracking, and detailed audit trails make it a strong contender for banks needing to meet regulatory demands efficiently.
When choosing a platform, banks should focus on their unique needs, regulatory obligations, and available resources to ensure the best fit for their compliance strategy.
sbb-itb-107f699
How to Set Up GRC Software
To implement GRC software for EU banks, focus on planning, assessing needs, and ensuring compliance with DORA requirements.
Requirements Analysis
Start by evaluating your current systems to identify compliance gaps and align with DORA requirements.
- Risk Assessment Framework: Conduct regular vulnerability assessments, perform Business Impact Analysis (BIA), evaluate third-party risks, and ensure integration with existing systems.
- Compliance Mapping: Match regulatory needs with software capabilities. Here's a quick breakdown:
| Requirement Category | Software Capabilities Needed | Priority Level |
|---|---|---|
| ICT Risk Management | Automated risk assessment tools | Critical |
| Incident Reporting | Real-time monitoring and alerts | High |
| Third-Party Management | Vendor risk assessment platform | Critical |
| Business Continuity | Automated backup and recovery | High |
- Resource Planning: Identify the technical infrastructure and personnel needed to support the system.
Once you've outlined these requirements, move on to configuring the system and training your team.
Setup and Training
"The GRC vendor selection process is complicated due to the wide range of requirements of various stakeholders involved in the process, such as BU heads of enterprise risk management, corporate compliance, IT and cyber security, credit risk management, and others."
During setup, configure access controls, integrate the software with existing banking systems, establish data migration protocols, set up automated reporting workflows, and ensure security measures align with DORA standards.
Provide role-specific training that covers platform operations, DORA compliance guidelines, and incident response procedures. After implementation and training, schedule regular updates to maintain compliance.
Updates and Maintenance
After the system is set up, use automated monitoring to track performance and compliance. Regular updates should address security patches, regulatory adjustments, feature improvements, and performance tuning.
Maintenance Schedule:
| Activity | Frequency | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Security Updates | Monthly | Vulnerability patches |
| Compliance Reviews | Quarterly | Regulatory alignment |
| System Audits | Bi-annual | Performance optimization |
| User Access Review | Monthly | Security verification |
Automated monitoring tools should keep an eye on system performance metrics, track regulatory updates, generate compliance reports, and alert stakeholders to any potential issues.
Additionally, conduct regular Threat-Led Penetration Testing (TLPT) to validate security measures, test third-party integrations, and assess business continuity procedures.
GRC Software Trends for 2025
AI in GRC Systems
Banks are set to increase their AI investments significantly, with spending projected to grow from $6 billion to $9 billion by 2025. This surge could add an estimated $200–340 billion annually to the global banking sector's value.
How AI Is Shaping GRC:
| Application Area | Impact | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Compliance Testing | Improved accuracy and coverage | Automated risk detection and checks |
| Regulatory Reporting | Streamlined report creation | Advanced pattern recognition |
Morgan Stanley Wealth Management provides a real-world example with its AI-powered Debrief tool. This solution saves advisors about 30 minutes per client meeting while ensuring compliance.
"The EU AI Act's requirements around bias detection, regular risk assessments, and human oversight aren't limiting innovation - they're defining what good looks like in financial services AI." – Diyan Bogdanov, Director of Engineering Intelligence & Growth, Payhawk
AI is taking earlier automation efforts further by simplifying compliance processes and risk assessments. This is particularly evident in areas like XBRL reporting and regulatory monitoring. While AI enhances efficiency, live monitoring tools complement this by reinforcing real-time risk management.
Live Monitoring Systems
Building on AI advancements, GRC platforms now offer real-time monitoring to meet the increasing demands of DORA compliance, especially in light of rising cyber threats. These systems provide continuous tracking and instant alerts, which are now critical for maintaining compliance.
Core Features of Live Monitoring Systems:
- Continuous Surveillance: Tracks performance and security metrics in real time.
- Automated Alerts: Sends immediate notifications for violations or threats.
- Audit Trail: Maintains comprehensive logs of system activities.
- Performance Analytics: Offers dashboards for compliance and risk insights.
"We estimate that with Dynatrace, organizations can automate up to 80% of the technical tasks necessary to be DORA compliant, helping reduce the overall required time and personnel by 50–70%. Unifying observability and security not only helps save significant time and effort, it also provides the necessary visibility into the organization's IT environment and helps to achieve continuous compliance." – Bernd Greifeneder, Founder and Chief Technology Officer, Dynatrace
Explainable AI (XAI) is also gaining traction in monitoring systems, with 36% of asset managers already using AI and another 37% planning to expand its use.
Key Focus Areas for Implementation:
| Monitoring Aspect | Primary Benefit | DORA Compliance Area |
|---|---|---|
| Security Monitoring | Real-time threat detection | ICT risk management |
| Performance Tracking | Tracks service availability | Operational resilience |
| Compliance Monitoring | Ensures regulatory adherence | Continuous compliance |
| Incident Response | Automates alert systems | Incident reporting |
These advanced monitoring tools are helping banks enhance their risk management strategies while staying aligned with evolving EU regulations.
Conclusion
EU banks need to adopt effective GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) software to meet 2025 regulatory demands and ensure smooth operations. With evolving technologies and stricter regulations, a thoughtful approach to GRC implementation is crucial.
Key Areas to Focus On:
| Focus Area | Priority | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Integration | Flexibility and scalability | Better operational performance |
| AI Adoption | Automated compliance | 34% boost in productivity |
| Continuous Monitoring | Real-time risk tracking | Faster incident response times |
| Third-party Oversight | Vendor risk management | Reduced supply chain vulnerabilities |
These areas are critical for a successful GRC rollout and should be carefully addressed.
Quick Reference Guide
Here’s a brief checklist for GRC implementation:
- Assess current processes and risk management frameworks.
- Choose a vendor offering DORA-compliant features and AI tools.
- Establish standardized risk assessment methods.
- Regularly test and update systems to stay compliant.
"As the financial sector moves into 2025, regulatory reporting continues to evolve, underscoring the delicate balance between financial stability, operational transparency, and market innovation." - Sébastien Polese, General Manager at SBS
The global push toward ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investments, expected to hit $34 trillion by 2026, highlights the growing need for adaptable GRC solutions. With 67% of companies planning to increase AI investments, banks must align their GRC strategies with both current demands and future regulations.
A well-executed GRC strategy is essential for meeting DORA requirements and maintaining operational success.


